Sunday, 26 June 2011
Network Administrator
A network administrator is a person who is responsible to maintain to hardware and software that comprise a network. It usually a technical or network staff in an organization but rarely involved with direct user support.
Network Operating Systems
Network Operating System is the software that runs on a server and enables the server to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. It allows to share files and printer access among multiple computers in a network, generally a local area network(LAN), or private network or to another network.
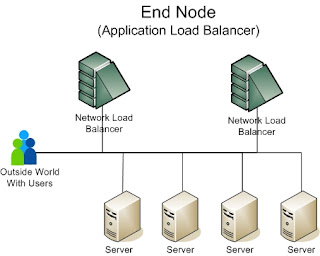
Server
A server is a computer program runs to serve the needs or request of other programs which may or may not be running on the same computer. often provide essential services across a network, either to private users inside a large organization or to public users via the internet.
Client
A client is an application or system that a remote service on another computer system, known as server, to connect the network. The device is not capable of running stand-alone programs, but interact with remote computers through a network.
Node
A node is a connection point, it depends on the network and protocol layer referred to. A physical network node is an active electronic device to connect to the network, and is capable of sending, receiving, or forwarding information over a communications channel.
TCP/IP
The TCP/IP (Internet Protocol Suite) is specific networking protocols which enable computer to communicate over a network. TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be formatted, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination.
Saturday, 25 June 2011
Demodulation
Demodulation is to extract the original information signal from modulated carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (normally defined radio) is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave. It widely used in connection with radio receivers as well.
Modulation
Modulatioon is the process of conveying a message signal. It used to transform a baseband message signal into passband signal. A device that performs modulation is known as a modulator, and a device that performs the inverse operation of modulation is known as a demodulator (sometimes detector or demod). A device that can do both operations is a modem (modulator–demodulator).
Friday, 24 June 2011
Chapter 9
Modulation
Demodulation
Bandwidth
TCP/IP
Node
Client
Server
Network Operating Systems
Network Administrator
Demodulation
Bandwidth
TCP/IP
Node
Client
Server
Network Operating Systems
Network Administrator
Monday, 20 June 2011
Solid-state storage
Solid-state storage devices have no moving parts. Data and information are stored and retrieved electronically directly from these devices. It commonly used in notebook computers, digital camera and digital video camera.
Optical disk drive
Optical disk drives hold over 50 gigabytes of data. There are three types : Compact Disc (CD), Digital Versatile Disc (DVD), and Hi-Def Disc. Compact Disc is optical format which memory from 650MB to 1GB capacity with rotation speeds vary. Digital Versatile Disc known as Digital Video Disc (DVD) which similar to CDs, but can store more data from 4.7GB to 17GB on the single disc. Hi-Def Disc is the next generation of optical disc which far greater capacity than DVDs.
Internet hard drive
Internet hard drives known as i-drive or online storage. It is low cost and can access information from any location using the Internet. Sometimes it is oriented to either business or individuals.
File compression & depression
File compression helps to speed up transmission of files from one computer system to another. Sending and receiving compressed files across the Internet is a common activity.
Disk caching
Disk caching improves hard disk performance by anticipating data needs. In modern disk drives, it includes a small amount of internal cache. Its function is similar to cache memory. When a program needs to access new data, the operating system first checks to see if the data is in the cache before reading it from the disk.
Sunday, 19 June 2011
optical-mark recognition
Optical-mark recognition (OMR) is the process of capturing human-marked data from document forms such as surveys and tests.
Optical-character recognition
Optical-character recognition (OCR) is the mechanical or electronic translation of scanned images of handwritten, typewritten or printed text into machine-encoded text. It is commonly used to convert books and documents into electronic files, to computerize a record-keeping system in an office, or to publish the text on a website.
Magnetic-ink
Magnetic-ink is a character recognition technology used primarily by the banking industry to facilitate the processing of cheques. The technology allows computers to read information (such as account numbers) off printed documents.
Laser printer
A laser printer is a common type of printer that print high quality text and images on plain paper. Laser printers do not use ink but they are able to print pages faster. Laser printers typically have a resolution of 600 dpi (dots per inch) or higher.
Ink-jet printer
Ergonomic Keyboard
An ergonomic keyboard is a computer keyboard which consider to minimize muscle strain and a host of related problems. It allows right and left hands to type at a slight angle more natural to the human form. Of course, this is much more expensive than the normal keyboard types.
Wednesday, 15 June 2011
Input and Output
Ergonomic Keyboard
Ink-jet printer
Laser printer
Magnetic-ink
Optical-character recognition
Optical-mark recognition
Secondary Storage
Disk Caching
File Compression
File Decompression
Internet hard drive
Optical Disc Drive
Solid-state Storage
Ink-jet printer
Laser printer
Magnetic-ink
Optical-character recognition
Optical-mark recognition
Secondary Storage
Disk Caching
File Compression
File Decompression
Internet hard drive
Optical Disc Drive
Solid-state Storage
Saturday, 28 May 2011
High Definition Multimedia Interface port
High Definition Multimedia Interface port (HDMI) is a audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data, normally used for high-end home theater systems.
Ethernet port
An Ethernet port is an opening on computer network equipment that Ethernet cables plug into. These ports are alternatively called jacks and sockets. Ethernet ports accept cables with RJ-45 connectors.
Firewire port
Parallel port
A parallel port is a type of interface which connects externel device such as printer. It is parallel communication physical interface.
Serial port
Serial port can be used in serial communication, in which only 1 bit is transmitted at a time. A serial port is a general-purpose interface, it can be used in almost any type of device.
Universal Serial Bus port (USB)
A USB port is a standard cable connection interface on personal computers and consumer electronics. USB ports allow stand-alone electronic devices to be connected via cables to a computer (or to each other). USB only has limited GB to save your own data, and it is small so you can bring it everywhere.
Friday, 27 May 2011
Plug and Play
Plug and Play (PnP) technology provides a combination of software and hardware support that enables the Windows operating system to detect and configure hardware with little or no user involvement. Plug and Play makes it easier to add and configure hardware on a computer, it supports wide range of devices.
Network Interface Card
A network interface card (NIC) is a computer circuit board or card that is installed in a computer so that it can be connected to a network. A network card commonly found in most desktop computers today that do not already have an integrated network on their motherboard.
Sound Card
A sound card also known as an audio card. It is an internal computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs. It also also applied to external audio interfaces that use software to generate sound. Typical uses of sound cards include providing the audio component for multimedia applications such as music composition, editing video or audio, presentation, education and entertainment (games) and video projection.
Graphic Card
Graphic card is a piece of hardware installed in a computer that is responsible for rendering the image on the computer’s monitor or display screen. The first consideration when buying a graphics card is to be sure it is capable of displaying the best resolution the monitor can support.
Thursday, 26 May 2011
Flash Memory
Flash memory (Flash RAM) offers a combination of the features of ROM and RAM. Flash memory is non-volatile, meaning no power is needed to maintain the information stored in the chip. Like RAM, it can be updated to store new information. Like ROM, it doesn't lose that information when power to the system is switched off. Flash memory used in wide range of application.
ROM
Wednesday, 25 May 2011
Cache
Cache (pronounced as cash) memory improves processing by acting as a temporary high-speed holding area between the memory and the CPU. If requested data is contained in a cache, this request can be served by reading the cache, which is faster.
RAM
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It holds the program (sequence of instuctions) and data that the CPU is presently processing. RAM is much faster to read from and write to than the other kinds of storage in a computer, the hard disk, floppy disk, and CD-ROM. When you turn on your computer, your operating system and other files will automatically load into RAM again, normally from your hard disk. It is wiser to save your document every few minutes.
System Unit
RAM
Cache
ROM
Flash Memory
Graphic Card
Sound Card
Network Interface Card
Plug and Play
Universal Serial Bus port (USB)
Serial port
Parallel port
Firewire port
Ethernet port
High Definition Multimedia Interface port (HDMI)
Cache
ROM
Flash Memory
Graphic Card
Sound Card
Network Interface Card
Plug and Play
Universal Serial Bus port (USB)
Serial port
Parallel port
Firewire port
Ethernet port
High Definition Multimedia Interface port (HDMI)
Monday, 2 May 2011
Web Authoring
Web authoring is to design and create a Web site, from writing the site's underlying code to writing the text to managing the site's upkeep. Web authoring systemcombines web file management and easy-to-use WYSIWYG web page editing.
Vector Image
In physics, a vector is a representation of both a quantity and a direction at the same time. In vector images, the file that results from a graphic artist's work is created and saved as a sequence of vector statements. instead of containing a bit in the file for each bit of a line drawing, a vector graphic file describes a series of points to be connected. One result is a much smaller file.
Multimedia
Multimedia is media and content that uses a combination of different content forms. The term can be used as a noun (a medium with multiple content forms) or as an adjective describing a medium as having multiple content forms.
Image Editor
Image editor is a program that provided variety of features from editing bit-mapped images. The difference between image editors and paint programs is not always clear-cut, but in general image editors are specialized for modifying bit-mapped images, such as scanned photographs, whereas paint programs are specialized for creating images.
HTML Editor
HTML editor is a application software for creating web pages. The HTML markup of web pages can be written with any text editor, it offers convenience and added functionally. HTML software is easy to use since it has a feature that is known as WYSIWYG. When you design web pages you want to use editor features that are simple to understand.
Desktop Publishing Program
Desktop Publishing Program is a tool for graphic designers and non-designers to create visual communications for professional or desktop printing as well as for online or on-screen electronic publishing. It also resulted in a wider range of low-cost, easy-to-use software that didn't require traditional design and prepress skills to understand and use.
Bitmap Image
Bitmap is a type of memory organization or image format that used to store digital images. Bitmap comes from map of bits, alont with pixmap. It commonly refer to similar concept of pixels. bitmap implies one bit per pixel, while pixmap is used for images with multiple bits per pixel.
Radio Editing Software
Radio editing software can help preparing and editing music for broadcast. This software also for cross fading, mixing or other DJ applications. Most products can perform format conversions, so you can take a clip from the Internet or an MP3 file and convert it to the format your station uses for broadcasting.
Utility Suites
Utility suites is a kind of system sofware to help analyze, configure, optimize and maintain the computer. It allows users to do things like creating text documents, playing games, listening to music or surfing the web. Utility suites usually focus on how the computer infrastruture operates. Most utilities perform a single task or a small range of tasks. Some utilities combined several features in one piece of sofware.
DBMS
DBMS is the database management system. It is a computer software which designed of managing databases that is installed on a system hard drive or network. It is possible to designate one or more database administrators who may control each function, as well as provide other users with various levels of administration rights. DBMS can be a way for people to communicate with each other.
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is an application that simulate a paper, accounting worksheet. Spreadsheet normally is used for financial information as they can recalculate the whole sheet automatically to a single cell. Most spreadsheet application can link one spreadsheet to another. A change made in one spreadsheet automatically affects other spreadsheets.
Word Processor
Word processor is a software that people use to create, edit, and print documents. The advantage of this software is you can make changes of the document without retyping the whole. It also providing some forms of what-you-see-is what-you-get editing. Microsoft is the most common word processing software.
Sunday, 1 May 2011
Graphical User Interface
Graphical user interface makes the program easier to use. Well-designed graphical use interfaces can free users from learning complex command languages. It is a computer program that enables communicating with a computer throught the use of symbols, visual metaphors, and pointing devices. It allows you let you interact by using a mouse rather than by having to type in keyboard commands. A GUI sometimes uses one or more metaphors for objects familiar in real life.
Wednesday, 27 April 2011
Basic and Specialized Application Software
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Word Processor
Spreadsheet
DBMS
Utility Suites
Radio Editing Software
Bitmap Image
Desktop Publishing Program
HTML Editor
Image Editor |
Multimedia
Vector Image
Web Authoring
Word Processor
Spreadsheet
DBMS
Utility Suites
Radio Editing Software
Bitmap Image
Desktop Publishing Program
HTML Editor
Image Editor |
Multimedia
Vector Image
Web Authoring
Friday, 22 April 2011
Internet Security Suite
Internet Security Suite is another rogue security program which was found out to be a member of a large group of malicious application currently propagated via the Internet by means of a Trojan. Internet Security Suite virus will be dropped on computers even without users approval. A Trojan mentioned is able to penetrate a PC by looking for software vulnerabilities which it will manipulate to be able to gain access on victims computer. It states that computer is having problems with presence of Trojan, virus and spyware. One common alert it will display is system alert.
Filter
In computer programming, a filter is a program or section of code that is designed to examine each input or output request for certain qualifying criteria and then process or forward it accordingly. filter is "pass-through" code that takes input data, makes some specific decision about it and possible transformation of it, and passes it on to another program in a kind of pipeline. Usually, a filter does no input/output operation on its own. Filters are sometimes used to remove or insert headers or control characters in data.
Plug-in
In computing, a plug-in (or plugin) is a set of software components that adds specific abilities to a larger software application. If supported, plug-ins enable customizing the functionality of an application. For example, plug-ins are commonly used in web browsers to play video, scan for viruses, and display new file types. Well-known plug-ins examples include Adobe Flash Player and QuickTime. Add-on is often considered the general term comprising snap-ins, plug-ins, extensions, and themes.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)