Sunday 26 June 2011
Network Administrator
A network administrator is a person who is responsible to maintain to hardware and software that comprise a network. It usually a technical or network staff in an organization but rarely involved with direct user support.
Network Operating Systems
Network Operating System is the software that runs on a server and enables the server to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. It allows to share files and printer access among multiple computers in a network, generally a local area network(LAN), or private network or to another network.
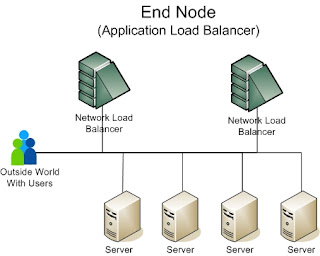
Server
A server is a computer program runs to serve the needs or request of other programs which may or may not be running on the same computer. often provide essential services across a network, either to private users inside a large organization or to public users via the internet.
Client
A client is an application or system that a remote service on another computer system, known as server, to connect the network. The device is not capable of running stand-alone programs, but interact with remote computers through a network.
Node
A node is a connection point, it depends on the network and protocol layer referred to. A physical network node is an active electronic device to connect to the network, and is capable of sending, receiving, or forwarding information over a communications channel.
TCP/IP
The TCP/IP (Internet Protocol Suite) is specific networking protocols which enable computer to communicate over a network. TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be formatted, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination.
Saturday 25 June 2011
Demodulation
Demodulation is to extract the original information signal from modulated carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (normally defined radio) is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave. It widely used in connection with radio receivers as well.
Modulation
Modulatioon is the process of conveying a message signal. It used to transform a baseband message signal into passband signal. A device that performs modulation is known as a modulator, and a device that performs the inverse operation of modulation is known as a demodulator (sometimes detector or demod). A device that can do both operations is a modem (modulator–demodulator).
Friday 24 June 2011
Chapter 9
Modulation
Demodulation
Bandwidth
TCP/IP
Node
Client
Server
Network Operating Systems
Network Administrator
Demodulation
Bandwidth
TCP/IP
Node
Client
Server
Network Operating Systems
Network Administrator
Monday 20 June 2011
Solid-state storage
Solid-state storage devices have no moving parts. Data and information are stored and retrieved electronically directly from these devices. It commonly used in notebook computers, digital camera and digital video camera.
Optical disk drive
Optical disk drives hold over 50 gigabytes of data. There are three types : Compact Disc (CD), Digital Versatile Disc (DVD), and Hi-Def Disc. Compact Disc is optical format which memory from 650MB to 1GB capacity with rotation speeds vary. Digital Versatile Disc known as Digital Video Disc (DVD) which similar to CDs, but can store more data from 4.7GB to 17GB on the single disc. Hi-Def Disc is the next generation of optical disc which far greater capacity than DVDs.
Internet hard drive
Internet hard drives known as i-drive or online storage. It is low cost and can access information from any location using the Internet. Sometimes it is oriented to either business or individuals.
File compression & depression
File compression helps to speed up transmission of files from one computer system to another. Sending and receiving compressed files across the Internet is a common activity.
Disk caching
Disk caching improves hard disk performance by anticipating data needs. In modern disk drives, it includes a small amount of internal cache. Its function is similar to cache memory. When a program needs to access new data, the operating system first checks to see if the data is in the cache before reading it from the disk.
Sunday 19 June 2011
optical-mark recognition
Optical-mark recognition (OMR) is the process of capturing human-marked data from document forms such as surveys and tests.
Optical-character recognition
Optical-character recognition (OCR) is the mechanical or electronic translation of scanned images of handwritten, typewritten or printed text into machine-encoded text. It is commonly used to convert books and documents into electronic files, to computerize a record-keeping system in an office, or to publish the text on a website.
Magnetic-ink
Magnetic-ink is a character recognition technology used primarily by the banking industry to facilitate the processing of cheques. The technology allows computers to read information (such as account numbers) off printed documents.
Laser printer
A laser printer is a common type of printer that print high quality text and images on plain paper. Laser printers do not use ink but they are able to print pages faster. Laser printers typically have a resolution of 600 dpi (dots per inch) or higher.
Ink-jet printer
Ergonomic Keyboard
An ergonomic keyboard is a computer keyboard which consider to minimize muscle strain and a host of related problems. It allows right and left hands to type at a slight angle more natural to the human form. Of course, this is much more expensive than the normal keyboard types.
Wednesday 15 June 2011
Input and Output
Ergonomic Keyboard
Ink-jet printer
Laser printer
Magnetic-ink
Optical-character recognition
Optical-mark recognition
Secondary Storage
Disk Caching
File Compression
File Decompression
Internet hard drive
Optical Disc Drive
Solid-state Storage
Ink-jet printer
Laser printer
Magnetic-ink
Optical-character recognition
Optical-mark recognition
Secondary Storage
Disk Caching
File Compression
File Decompression
Internet hard drive
Optical Disc Drive
Solid-state Storage
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)